Lab Topology:
Please use the following topology to complete this lab exercise:
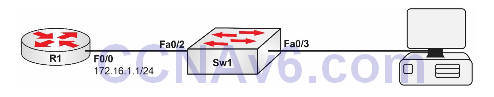
Task 1:
Configure the hostnames on R1 and Sw1 as illustrated in the topology.
Task 2:
Configure VLAN50 named DHCP_VLAN on Sw1. Assign the FastEthernet0/2 and FastEthernet0/3 interfaces on Sw1 to this VLAN. Ensure that the ports immediately transition to the Spanning Tree Forwarding state. This is actually an ICND2 requirement but I’ve slipped it in here (we’ll do a PortFast lab in the ICND2 section).
Task 3:
Configure R1 as a Cisco IOS DHCP server with the following settings:
- DHCP pool name: CCNA-DHCP-POOL
- DHCP network: 172.16.1.0/24
- DNS server: 10.1.1.254
- WINS server: 10.2.2.254
- Default gateway: 172.16.1.1
- DNS domain: howtonetwork.net
- DHCP lease time: 5 days 30 minutes
Some of the options above are not available in Packet Tracer, so you may want to use GNS3.
Ensure that you exclude the IP address of the router interface from the DHCP pool.
Task 4:
Verify your DHCP configuration on the connected workstation (or other DHCP client) and verify that your Cisco IOS DHCP server is showing a leased DHCP address.
Configuration and Verification
Task 1:
For reference information on configuring hostnames, please refer to earlier labs.
Task 2:
Sw1#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z.
Sw1(config)#vlan50
Sw1(config-vlan)#name DHCP_VLAN
Sw1(config-vlan)#exit
Sw1(config)#interface range fastethernet0/2 – 3
Sw1(config-if-range)#switchport mode access
Sw1(config-if-range switchport access vlan50
Sw1(config-if-range)#spanning-tree portfast
%Warning: portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc... to this interface when portfast is enabled, can cause temporary bridging loops.
Use with CAUTION
%Portfast will be configured in 2 interfaces due to the range command
but will only have effect when the interfaces are in a non-trunking mode.
Sw1(config-if-range)#no shutdown
Sw1(config-if-range)#end
Sw1#
Task 3:
R1#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z.
R1(config)#ip dhcp pool CCNA-DHCP-POOL
R1(dhcp-config)#network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
R1(dhcp-config)#dns-server 10.1.1.254
R1(dhcp-config)#netbios-name-server 10.2.2.254
R1(dhcp-config)#default-router 172.16.1.1
R1(dhcp-config)#domain-name howtonetwork.net
R1(dhcp-config)#lease 5 0 30
R1(dhcp-config)#exit
R1(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 172.16.1.1
R1#show ip dhcp pool CCNA-DHCP-POOL
Pool CCNA-DHCP-POOL :
Utilization mark (high/low) : 100 / 0
Subnet size (first/next) : 0 / 0
Total addresses : 254
Leased addresses : 0
Excluded addresses : 1
Pending event : none
1 subnet is currently in the pool
Current index IP address range Leased/Excluded/Total
172.16.1.1 172.16.1.1 - 172.16.1.254 0 / 1 / 254
Task 4:
I used another router as a DHCP client, as you can see below. If you use a host, then configure it to obtain the IP address via DHCP.
Router(config)#int f0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address dhcp
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%DHCP-6-ADDRESS_ASSIGN: Interface FastEthernet0/0 assigned DHCP address 172.16.1.2, mask 255.255.255.0, hostname Router3
Router#show ip dhcp binding
IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type Hardware address
172.16.1.2 0060.47BC.7A01 -- Automatic
The ipconfig /all command on a Windows-based workstation would show the following:
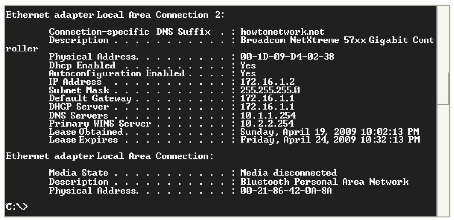
NOTE: If you have configured another Cisco IOS device as a DHCP client to test your configuration, you should see the following output:
Router#show ip dhcp pool
Pool CCNA-DHCP-POOL :
Utilization mark (high/low) : 100 / 0
Subnet size (first/next) : 0 / 0
Total addresses : 254
Leased addresses : 1
Excluded addresses : 1
Pending event : none
1 subnet is currently in the pool
Current index IP address range Leased/Excluded/Total
172.16.1.1 172.16.1.1 - 172.16.1.254 1 / 1 / 254